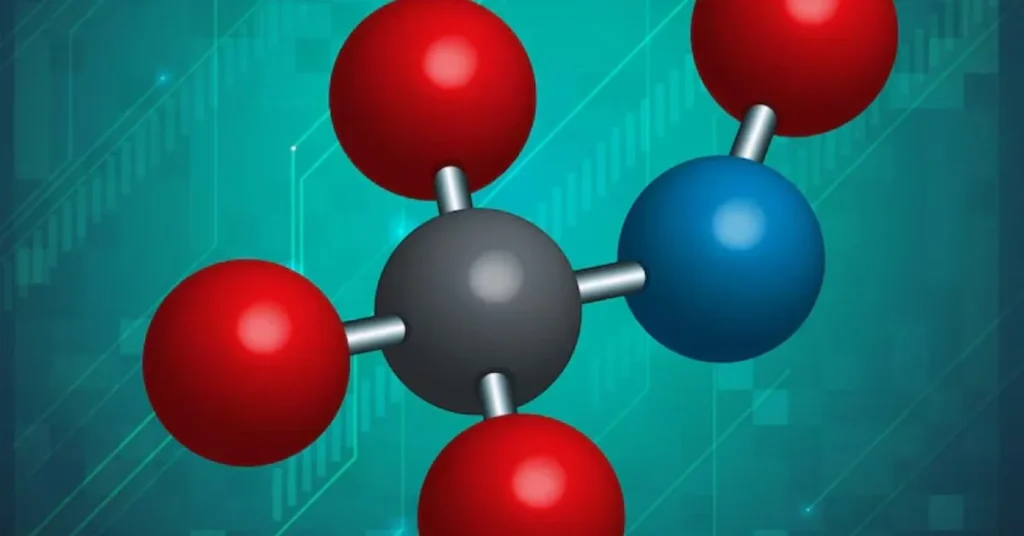
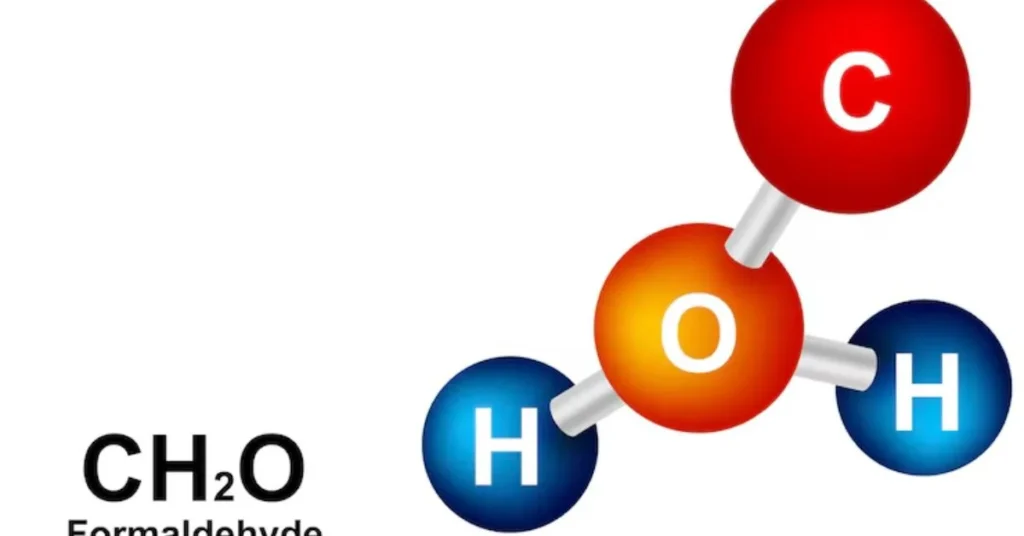
At first look, the chemical formula HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O may not make much sense. However, for those well-versed in ester chemistry, it indicates an interesting and useful reaction: the hydrolysis of methyl formate when water is present. This process is of great interest to scientists and has significant industrial implications despite its apparent chemical simplicity.
From its chemical structure and reaction routes to its practical uses and green chemistry implications, this article will cover it everything. This tutorial provides a thorough explanation of the relevance of this reaction for anybody interested in chemistry, whether they are students, professionals, or just plain inquisitive.
What Does HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O Represent?
This chemical shorthand combines a formulaic description of an ester (methyl formate) with water, hinting at a hydrolysis reaction. Properly structured, the equation is:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
Here’s what each part means:
- HCOOCH₃ = Methyl Formate, an ester
- H₂O = Water
- HCOOH = Formic Acid
- CH₃OH = Methanol
This is a classic ester hydrolysis reaction, where an ester breaks down into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of water. Depending on conditions, this can be acid- or base-catalyzed.
Understanding the Hydrolysis Reaction
Hydrolysis is the breaking of chemical bonds by the use of water. During hydrolysis, the ester bond between the formyl (HCO) and methyl alcohol components of methyl formate (HCOOCHₜ) is broken.
General Reaction
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
In simpler terms:
- The ester (methyl formate) reacts with water.
- The bond between the carbon and the oxygen (linking the formate and methyl groups) breaks.
- The end products are formic acid and methanol.
This reaction is central to many industrial processes where conversion of esters to more reactive or useful forms is desired.
Chemical Properties of the Reactants and Products
To understand the chemistry better, let’s look at the key players involved:
Table of Key Compounds
| Compound | Formula | Boiling Point (°C) | Solubility | Physical Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl Formate | HCOOCH₃ | 31.5 | Soluble in water | Colorless, flammable liquid |
| Water | H₂O | 100 | Universal solvent | Colorless, odorless liquid |
| Formic Acid | HCOOH | 100.8 | Completely miscible with water | Clear liquid with pungent odor |
| Methanol | CH₃OH | 64.7 | Miscible with water | Clear, volatile liquid |
Detailed Mechanism of Hydrolysis
The hydrolysis of methyl formate can be catalyzed by both acids and bases. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown under acidic conditions:
Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Protonation of Ester: The carbonyl oxygen of the ester is protonated by an acid, increasing electrophilicity.
- Nucleophilic Attack: Water acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon.
- Tetrahedral Intermediate: A tetrahedral intermediate forms briefly.
- Proton Transfer: The intermediate rearranges via proton shifts.
- Leaving Group Ejection: Methanol is expelled.
- Deprotonation: The final product is formic acid.
This efficient and elegant mechanism is used in synthetic chemistry and industrial conversions.
Factors Affecting the Reaction Rate
Several variables influence how fast and efficiently this hydrolysis occurs:
Key Factors
- Catalysts: Both acids (HCl, H₂SO₄) and bases (NaOH) can catalyze the reaction.
- Temperature: Heating the mixture speeds up molecular motion and accelerates the reaction.
- Water Concentration: Excess water shifts equilibrium towards the products.
- Solvent Choice: Aqueous and polar solvents help stabilize intermediates.
Adjusting these parameters allows chemists to fine-tune reaction speed and yield.
Applications in Industry
The simplicity of the hydrolysis reaction belies its wide-ranging applications:
1. Formic Acid Manufacturing
Formic acid is used in:
- Leather tanning
- Textile dyeing
- Agriculture (as a preservative)
- Rubber production
2. Methanol Recovery
Methanol finds roles as:
- A fuel and antifreeze agent
- A precursor for formaldehyde
- A solvent in pharmaceutical synthesis
3. Controlled Ester Breakdown
Methyl formate is used as an intermediate in the production of:
- Dimethylformamide (DMF)
- Formamides
- Organic solvents
These applications underline the significance of controlled ester hydrolysis.
Safety and Handling Considerations
As useful as this chemistry is, the compounds involved come with safety requirements.
Methyl Formate
- Highly flammable
- Vapor can cause dizziness
- Should be stored in sealed containers away from heat
Formic Acid: HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
- Corrosive to skin and eyes
- Vapors are irritating
- Requires proper PPE when handling
Methanol
- Toxic when ingested
- Can cause blindness or death
- Requires ventilated spaces and safety goggles
General Safety Tips: HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
- Always work in a fume hood or ventilated area.
- Use gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
- Know emergency protocols for spills or exposure.
Environmental Relevance and Green Chemistry
This reaction is also significant from an environmental and sustainability standpoint.
Benefits in Green Chemistry
- Mild Conditions: The reaction doesn’t require high temperatures or pressures.
- Water as Solvent: Water is eco-friendly and widely available.
- Recyclable By-products: Methanol can be reclaimed and reused.
Future Outlook
- Bio-based production of methyl formate from CO₂ and methanol
- Low-emission methods for large-scale hydrolysis
- Catalysts that reduce energy input
These improvements align with modern goals of minimizing chemical waste and optimizing resource use.
Conclusion: HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
Despite its seeming simplicity, the HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O reaction is profoundly important for both theoretical understanding and practical applications in industry. While seemingly insignificant, this hydrolysis reaction plays a crucial role in contemporary chemistry by providing a route for environmentally friendly chemical processes and generating essential molecules such as formic acid and methanol.
Whether you’re a lab technician, a manufacturing process manager, or simply an organic chemistry student, this information will help you comprehend and value the chemical changes that occur in your daily life.
FAQs: HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
1. What is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O?
It represents the hydrolysis of methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) in the presence of water, producing formic acid and methanol.
2. Is the hydrolysis of methyl formate reversible?
Yes, under specific conditions, the reverse reaction (esterification) can occur.
3. What are the industrial uses of this reaction?
This reaction is used to produce formic acid and methanol, both valuable in various industrial processes.
4. Is methyl formate toxic?
Yes. While useful, methyl formate is flammable and its vapors are harmful. Proper handling is essential.
5. Can this reaction be used in green chemistry?
Absolutely. The use of water as a solvent and potential for bio-based feedstocks make it ideal for sustainable chemical engineering.
For more information, click here.