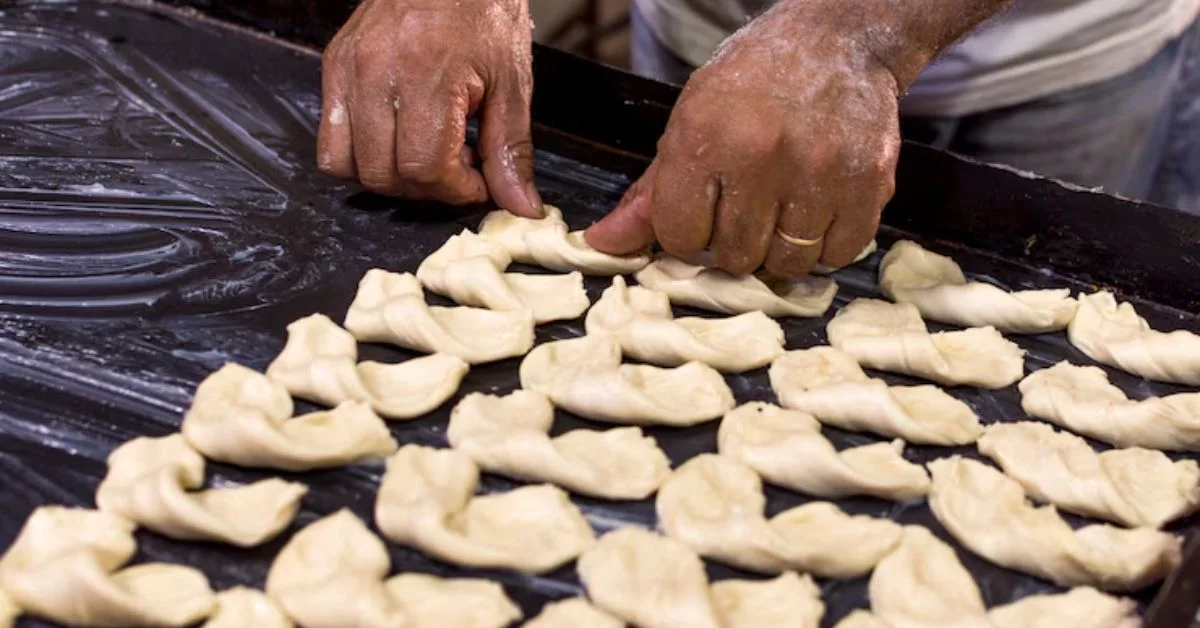
In the heart of Italy and in commercial kitchens around the world, one piece of culinary equipment is quietly redefining the pace and precision of fresh pasta production: the tortellinatrice. If you’re wondering what a tortellinatrice is, how it works, or why it’s suddenly appearing in both artisanal kitchens and industrial food facilities, you’re asking the right questions at a pivotal time in food technology.
A tortellinatrice is a specialized machine designed to automate the creation of tortellini, the iconic ring-shaped stuffed pasta originating from the Emilia-Romagna region. But today, it represents more than just mechanized production—it is the convergence of culinary heritage and automation, meeting the demands of global markets, local traditions, and evolving labor realities.
This comprehensive exploration of the tortellinatrice reveals how it works, its applications, cultural relevance, technical innovations, and its growing footprint in 2025. Whether you’re a pasta enthusiast, a food manufacturer, or a chef running a small trattoria, understanding this machine can change how you view pasta altogether.
What Is a Tortellinatrice?
A tortellinatrice is a pasta-making machine specifically engineered to produce tortellini by automating the folding, filling, and shaping process. Traditional tortellini—typically stuffed with meat, cheese, or vegetables—are hand-folded into their distinctive navel shape. While this is ideal for home cooking or boutique production, it’s time-intensive and difficult to scale.
Enter the tortellinatrice. The machine handles:
- Sheet rolling: Flattening pasta dough to a uniform thickness
- Filling: Depositing precise portions of filling onto the sheet
- Folding and shaping: Sealing and forming the signature tortellini ring shape
While early versions of the machine were strictly industrial, modern tortellinatrici (plural) come in various sizes and complexity levels—some suitable for countertop use in small restaurants, others capable of turning out tens of thousands of pieces per hour.
Origins and Evolution of the Tortellinatrice
The first rudimentary tortellinatrice emerged in post-war Italy during a period of economic growth and rising demand for packaged foods. These machines were originally large and loud, built for speed rather than finesse.
Timeline Highlights:
- 1950s–60s: First industrial tortellini machines created in Modena and Bologna
- 1980s: Introduction of machines with adjustable filling ratios
- 2000s: Emergence of semi-automatic machines for small food producers
- 2020s–2025: AI-assisted, hygienic, compact models for commercial and domestic use
Today’s tortellinatrice reflects both culinary sensitivity and technological sophistication. The best models replicate the look and feel of hand-folded pasta, using algorithms to manage dough elasticity and moisture consistency.
How the Tortellinatrice Works
Understanding how the tortellinatrice operates helps to appreciate its engineering complexity and culinary precision.
Step-by-Step Functionality:
- Dough Input and Rolling
- Pasta dough is loaded and passed through rollers that flatten it to a predefined thickness.
- Some models allow for dual-sheet input for layered stuffing.
- Filling Dispensation
- Filling is stored in a hopper and injected or deposited onto the sheet via calibrated nozzles.
- AI-enhanced models adjust based on dough tension and temperature.
- Cutting and Shaping
- The sheet moves through a mold that cuts and folds each portion into the ring shape.
- Sealing pressure is regulated to avoid burst pasta during cooking.
- Ejection or Conveyor Output
- Finished tortellini are either dropped into trays or passed along conveyors for drying or freezing.
Advanced tortellinatrici are often integrated with vacuum pumps, sterile air jets, or UV sterilization for food safety, especially in large-scale production settings.
Who Uses Tortellinatrici in 2025?
The use of tortellinatrici has expanded dramatically due to labor shortages, demand for artisanal-quality convenience food, and an uptick in global pasta consumption.
Key Users:
- Industrial Pasta Producers
- Large factories use high-capacity machines to produce for frozen food markets or packaged goods.
- Gourmet Delis and Restaurants
- Semi-automatic models allow chefs to maintain quality while increasing volume during peak hours.
- Culinary Schools
- Used for training students in both traditional pasta making and modern kitchen tech.
- Home Chefs (Niche Market)
- High-end, compact tortellinatrici are available for culinary hobbyists and food influencers.
The 2025 market includes models designed for every tier—from manually operated rollers to fully automated smart machines linked to inventory systems.
Benefits of Using a Tortellinatrice
Why would a pasta maker choose a machine over the age-old method of hand-folding?
1. Speed
- A manual operator can make about 100–150 tortellini per hour. A tortellinatrice can produce thousands.
2. Precision
- Uniformity in size and weight ensures even cooking and professional presentation.
3. Cost Efficiency
- Reduces labor hours, minimizes filling waste, and improves yield in commercial settings.
4. Hygiene
- Minimizes human contact, ideal for HACCP-certified facilities and modern kitchen codes.
5. Scalability
- Lets businesses expand offerings without a proportional increase in labor.
Despite these advantages, many chefs still see the tortellinatrice as a complement, not a replacement, to the art of pasta making.
Technological Advances in 2025
Modern tortellinatrici integrate cutting-edge technologies to enhance usability and performance.
AI and Machine Learning
- Detects inconsistencies in dough texture or filling density and adjusts mid-cycle.
- Learns operator preferences for shaping nuances.
IoT Integration
- Machines are connected to cloud dashboards for real-time diagnostics and output reports.
- Enables remote troubleshooting and predictive maintenance alerts.
Sustainability Features
- Uses recyclable components and energy-efficient motors.
- Some models are solar-compatible for rural settings.
These updates make the tortellinatrice a key player in the broader movement toward smart kitchens and sustainable food production.
Impact on Culinary Culture
There was once a concern that mechanizing tortellini might dilute Italy’s rich pasta heritage. But in reality, the opposite has occurred.
Cultural Preservation Through Access
- Regional tortellini recipes once confined to family kitchens can now be scaled and shared widely.
- Restaurants across continents can offer authentic tortellini without importing skilled pasta makers.
Empowering Artisans
- Small producers can increase volume without sacrificing integrity, keeping local businesses alive.
- Allows pasta artisans to focus on flavor and filling innovation, not just production logistics.
Global Fusion
- Tortellinatrici are now used to create fusion variants—like masala-spiced tortellini or Korean bulgogi-stuffed versions—enabling creativity while preserving form.
Rather than replacing the old ways, the tortellinatrice is helping them survive in a world that moves faster and expects more.
Cost and Market Trends
As of 2025, prices vary dramatically based on type and functionality:
| Type | Average Cost (USD) | Target User |
| Manual/Semi-automatic | $800–$2,500 | Small delis, culinary schools |
| Fully Automatic | $5,000–$25,000 | Restaurants, catering services |
| Industrial | $50,000–$150,000+ | Frozen food manufacturers |
Market research shows a 12% year-on-year growth in pasta-making equipment, with the tortellinatrice segment outpacing all others due to rising global interest in traditional foods made modern.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Operating a tortellinatrice is not plug-and-play. It requires:
- Regular sanitation with food-safe solvents
- Blade sharpening or mold replacement every few months
- Filling viscosity calibration, especially when switching recipes
- Staff training to avoid damage and ensure consistent output
Manufacturers now offer training modules, digital manuals, and on-site support to help operators make the most of their investment.
Conclusion
In the grand story of food innovation, the tortellinatrice stands as a shining example of how technology can honor tradition rather than replace it. It’s not about speeding up for the sake of speed but about making iconic foods more accessible, consistent, and sustainable.
For chefs seeking precision, businesses seeking efficiency, or communities seeking to preserve culinary identity, the tortellinatrice answers a modern question with old-world charm. As kitchens continue to evolve, machines like this will not erase the cook’s touch—they will enhance it, replicate it, and help it travel further than ever before.
FAQs
1. Is using a tortellinatrice considered authentic in Italian cuisine?
Yes, many Italian chefs use tortellinatrici to scale production while maintaining recipe authenticity and quality standards.
2. Can I use a tortellinatrice at home?
Absolutely. There are compact, user-friendly models designed for home use, especially for culinary hobbyists and small-batch makers.
3. How long does it take to learn to operate a tortellinatrice?
Most operators can learn basic functions in a few hours, but advanced models may require formal training or tutorials.
4. Can the machine handle non-traditional fillings like vegan or gluten-free options?
Yes, modern machines can be calibrated for different fillings, though testing is needed to adjust consistency and seal strength.
5. Where can I buy a tortellinatrice in 2025?
From specialty kitchen equipment retailers, online marketplaces, or directly from manufacturers in Italy, Germany, or North America.
For more information, click here.