Dental health plays a vital role in maintaining overall well-being. Among the various procedures available to preserve teeth and prevent decay, Preventive Resin Restoration (PRR) has become one of the most effective, conservative, and reliable treatments in modern dentistry. Unlike traditional fillings that are placed after significant decay has already damaged a tooth, preventive resin restoration is specifically designed to stop cavities at the earliest stage and protect teeth before they require extensive treatment.
The approach behind PRR is preventive rather than corrective, meaning it is applied before the tooth suffers major structural damage. This method not only saves time and cost but also ensures that more of the natural tooth structure is preserved. Over the years, it has gained popularity as parents, dentists, and patients have recognized its importance in preventing tooth decay in children, adolescents, and even adults who are at higher risk of cavities.
This article will provide a comprehensive and in-depth explanation of preventive resin restoration, including what it is, how it works, its benefits, its procedure, aftercare, and its long-term impact on dental health.
What is Preventive Resin Restoration?
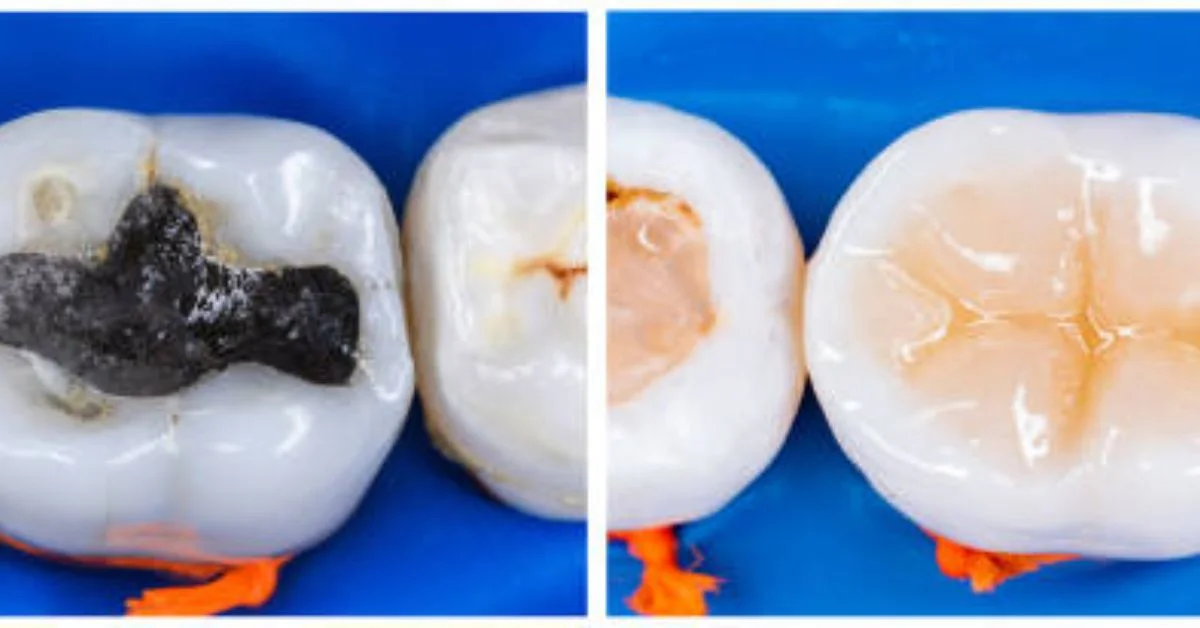
Preventive Resin Restoration (PRR) is a conservative dental treatment that combines elements of dental sealants and fillings. It is used to protect the chewing surfaces of teeth, primarily molars and premolars, which are more susceptible to decay due to their grooves, pits, and fissures.
The idea behind PRR is straightforward: when a tooth shows early signs of decay, such as demineralization or small carious lesions confined to the enamel, the dentist removes the affected portion and seals the area with a resin-based material. This prevents the lesion from progressing deeper into the dentin and pulp, where more invasive treatment like root canals or crowns may later be required.
Unlike conventional fillings that require significant drilling, PRR involves minimal removal of tooth structure. The procedure uses modern adhesive resin technology, which bonds strongly to the enamel, ensuring durability and protection against future decay.
The Need for Preventive Resin Restoration
Teeth are constantly exposed to bacteria, acids, and food debris that can lead to cavities if not properly managed. Children and teenagers are particularly vulnerable due to the eruption of new permanent molars, which often have deep grooves that are hard to clean with a toothbrush.
Traditional dental sealants protect teeth but do not address areas where decay has already started. On the other hand, regular fillings may be too aggressive for very small lesions, leading to unnecessary removal of healthy tooth material. PRR bridges this gap by offering a targeted treatment that removes only the decayed part and seals the tooth surface for protection.
Indications for Preventive Resin Restoration
Dentists recommend PRR in specific cases where there is a balance between preventive care and minimal intervention. It is particularly useful in the following situations:
- Early carious lesions confined to enamel or shallow dentin.
- Children and teenagers with recently erupted molars or premolars prone to decay.
- Patients with high caries risk, such as those with poor oral hygiene or a history of frequent cavities.
- Deep pits and fissures that cannot be effectively cleaned with regular brushing.
- Initial discoloration of enamel surfaces where decay has just begun.
The Procedure of Preventive Resin Restoration
The PRR procedure is relatively simple and quick compared to traditional restorative methods. It usually takes place in a single dental visit and involves the following steps:
- Diagnosis and Examination: The dentist examines the tooth using visual inspection, dental probes, and sometimes diagnostic tools such as laser fluorescence or radiographs. If decay is detected in its early stage, PRR is chosen as the treatment.
- Cleaning the Tooth Surface: The tooth is thoroughly cleaned to remove plaque, food particles, and debris. This ensures that the surface is free of contaminants before the resin is applied.
- Removal of Caries: The dentist uses a small drill, air abrasion, or laser to gently remove the decayed portion of the tooth. Only the affected enamel is removed, leaving the healthy structure intact.
- Etching and Bonding: The cleaned tooth surface is treated with an acidic gel (etchant) to create microscopic pores. This step enhances the bonding strength of the resin material to the enamel. A bonding agent is then applied to ensure adhesion.
- Application of Resin Material: The resin composite material is carefully placed into the prepared cavity or fissure. The material is then shaped and smoothed to blend with the tooth surface.
- Curing with Light: A special curing light is used to harden the resin, ensuring that it bonds firmly with the tooth structure.
- Polishing and Finishing: The restoration is polished to achieve a smooth surface that resists plaque accumulation and feels natural to the patient.
Materials Used in Preventive Resin Restoration
The effectiveness of PRR largely depends on the materials used. Typically, dentists use resin composites that are designed to mimic the natural appearance and strength of enamel. These materials are available in different shades, allowing the restoration to blend seamlessly with the natural tooth color.
Some PRRs may also incorporate fluoride-releasing resins, which provide added protection against cavities by strengthening the surrounding enamel.
Benefits of Preventive Resin Restoration
The popularity of PRR stems from the numerous advantages it offers to both patients and dentists.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Conservative Treatment | Preserves more natural tooth structure compared to traditional fillings. |
| Prevents Decay Progression | Stops cavities from spreading deeper into dentin or pulp. |
| Aesthetic Appearance | Resin blends with natural tooth color for an invisible restoration. |
| Quick and Painless Procedure | Requires minimal drilling and often no anesthesia. |
| Long-Term Protection | Seals grooves and fissures against bacterial invasion and acid attack. |
| Cost-Effective | Less expensive than extensive restorative procedures like crowns or root canals. |
| Suitable for Children | Ideal for protecting newly erupted permanent molars. |
Difference Between Sealants, Fillings, and PRR
It is important to understand how preventive resin restoration differs from other dental procedures such as sealants and fillings.
| Aspect | Sealants | PRR | Fillings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents cavities in healthy teeth | Prevents and treats very early cavities | Repairs advanced cavities |
| Tooth Preparation | No removal of tooth structure | Minimal removal of decayed enamel | Moderate to extensive drilling |
| Material | Sealant resin | Resin composite | Amalgam or resin composite |
| Aesthetic | Usually tooth-colored | Tooth-colored | Tooth-colored or metallic |
| Longevity | Several years with proper care | Durable with longer-term protection | Long-lasting depending on size and material |
Longevity and Durability of PRR
When properly done, preventive resin restorations can last many years. Their longevity depends on factors such as:
- Quality of the material used.
- The dentist’s technique and precision.
- Patient’s oral hygiene habits.
- Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings.
In most cases, PRRs last anywhere from 5 to 10 years, and with good care, sometimes even longer.
Aftercare for Preventive Resin Restoration
Maintaining PRRs requires similar care to natural teeth. Patients should:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to prevent decay between teeth.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks to reduce acid exposure.
- Visit the dentist regularly for checkups and professional cleaning.
- Avoid chewing very hard foods (like ice or hard candy) that can damage restorations.
Preventive Resin Restoration for Children
PRRs are particularly beneficial for children. As permanent molars erupt around the ages of 6 and 12, they are highly prone to decay due to deep pits and grooves. Applying PRRs shortly after eruption provides long-term protection, reduces the risk of cavities, and minimizes the need for future dental interventions.
Parents are encouraged to discuss PRR with pediatric dentists to safeguard their children’s dental health.
Preventive Resin Restoration for Adults
Though PRR is more commonly associated with children and teenagers, adults can also benefit. Adults with high caries risk, deep fissures, or early enamel lesions can receive PRRs to prevent further decay. In fact, adults who have undergone orthodontic treatments or who suffer from dry mouth conditions are often good candidates for PRRs.
Cost Considerations
The cost of PRR is generally lower than that of larger restorative procedures such as crowns or root canals. While prices vary based on location, dentist expertise, and materials used, PRRs are typically affordable and are often covered by dental insurance, especially for children. The relatively low cost combined with long-term benefits makes PRR an excellent investment in dental health.
Limitations of Preventive Resin Restoration
While PRR is highly effective, it is not suitable in all cases.
- It cannot be used for advanced decay that has reached the dentin or pulp.
- Requires careful diagnosis to avoid undertreatment or overtreatment.
- Durability may vary depending on patient habits and maintenance.
- Regular monitoring is necessary to ensure the restoration continues to protect the tooth.
The Future of Preventive Resin Restoration
Advancements in dental materials and techniques continue to improve PRR. Future trends may include:
- Nanotechnology-based resins that enhance strength and durability.
- Fluoride-releasing composites that actively fight decay.
- Laser-assisted caries removal, making the procedure even less invasive.
- Digital diagnostics that allow earlier detection of cavities, making PRR applicable to more patients.
Conclusion
Preventive Resin Restoration represents one of the most important developments in conservative dentistry. By addressing cavities in their earliest stage and sealing vulnerable surfaces, PRR protects teeth, maintains natural structure, reduces the need for invasive procedures, and contributes to long-term oral health. Whether for children with newly erupted molars or adults at risk of cavities, PRR serves as a cost-effective and reliable preventive measure.
By understanding its process, benefits, and care requirements, patients and parents can make informed decisions about incorporating preventive resin restorations into their dental care routine.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of preventive resin restoration?
Its main purpose is to stop early decay from progressing while protecting tooth surfaces against future cavities.
2. How long do preventive resin restorations last?
With proper care, PRRs can last 5–10 years or more, depending on materials and oral hygiene practices.
3. Are preventive resin restorations painful?
No, the procedure is usually painless since it involves minimal drilling and often does not require anesthesia.
4. Can adults benefit from PRR?
Yes, adults with deep grooves, early enamel lesions, or high cavity risk can also benefit from PRR treatment.
5. How is PRR different from a regular filling?
PRR treats very early decay with minimal drilling, while fillings are for larger cavities that require more extensive tooth removal.
For more information, click here.